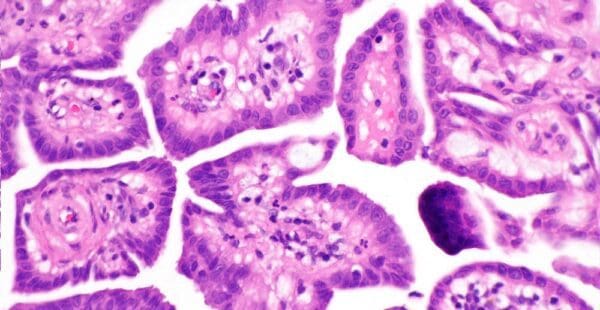
What Is Papillary Mesothelioma?
Papillary mesothelioma, also called well-differentiated papillary mesothelioma (WDPM), is a rare subtype of epithelial mesothelioma. It most often occurs in the lining of the abdomen (peritoneum). Less often, it may occur in the linings of the lungs (pleura) or testicles (tunica vaginalis).
Characteristics of papillary mesothelioma include:
- Cell growth: WDPM cell growth is slow and microscopic. This growth pattern differentiates epithelial mesothelioma from malignant sarcomatoid mesothelioma. In contrast, sarcomatoid cells exhibit aggressive behavior and rapid growth.
- Cell pattern: WDPM cells can be round or oval. The cells form finger-like projections called papillae.
- Patient demographic: WDPM is most common in young women, especially those with a history of endometriosis and ovarian cancer.
- Tumor location: Papillary mesothelioma affects cells in the linings of internal organs.
- Unique calcification: In rare cases, papillary cancers may form psammoma bodies. Psammoma bodies are areas of calcification within the tumor.
Identifying tumor cell characteristics can help differentiate papillary mesothelioma from other mesothelioma subtypes.
Is Papillary Mesothelioma Benign?
Papillary mesothelioma is typically benign.
Some researchers have reported WDPM becoming malignant over a period of years. However, others have concluded WDPM is not a precursor to malignant mesothelioma. Conflicting information may be due to initial misdiagnosis of malignant mesothelioma as WDPM.
WDPM does not usually recur after it is treated because it is normally benign. Patients often experience no symptoms and live many years with this condition.
Well-Differentiated Papillary Mesothelioma and Asbestos
Papillary mesothelioma has been linked to asbestos exposure. In a review of 24 pleural WDPM cases, half of the patients had confirmed occupational asbestos exposure.
Published cases of papillary mesothelioma are rare. The disease is prone to misdiagnosis or being left undiagnosed altogether. These factors make the condition difficult to study.
Asbestos exposure itself is also difficult to track. Occupational asbestos exposure is the most common cause of mesothelioma. However, individuals may be exposed at home, school and many other locations.
It is difficult to measure how often people exposed to asbestos develop papillary mesothelioma because there is so little data.
Papillary Mesothelioma Symptoms
The majority of patients diagnosed with papillary mesothelioma show no symptoms.
One MD Anderson Cancer Center study reviewed 26 female patients with papillary mesothelioma. In this study, only two patients presented symptoms. However, any reported symptoms can help physicians reach an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnosing Well-Differentiated Papillary Mesothelioma
Papillary mesothelioma diagnosis often occurs incidentally during other procedures. This means doctors often find it when performing other procedures on a patient.
However, well-differentiated papillary mesothelioma can be discovered in several ways, including:
- Biopsies: Tissue biopsies may help diagnose WDPM. These include laparoscopic biopsy, open biopsy and thoracoscopic biopsy.
- Histology and pathology: Microscopic analysis of biopsy samples can identify WDPM.
- Imaging scans: X-rays and CT scans can help identify WDPM tumors.
- Immunohistochemistry: This process uses special dyes to identify unique cell proteins.
These methods may be combined to confirm a diagnosis. However, biopsies are the only way to definitively diagnose papillary mesothelioma. A biopsy can characterize tumor cells, including mesothelioma type and stage. Biopsies are crucial for an accurate diagnosis. They can also help prevent cancer misdiagnosis.
To prevent misdiagnosis, physicians may also observe symptoms and common co-occurring conditions.
Conditions associated with papillary mesothelioma include:
- Colorectal cancer
- Endometriosis
- Ovarian cancer
The presence of the conditions in conjunction with WDPM has been observed in a few patients. There is not enough data for the conditions to be considered risk factors for mesothelioma. However, they may assist doctors with correctly diagnosing papillary mesothelioma.
Accurate diagnosis is important to ensure the disease is treated correctly.
What Is the Prognosis for Papillary Mesothelioma?
WDPM is typically benign and has a very favorable mesothelioma prognosis. Patients may survive for years or decades. The most common type of WDPM, which affects the peritoneum, has a 5-year survival rate of 90% with treatment. This means that about 90% of patients are still alive 5 years after diagnosis.
In the MD Anderson Cancer Center study of 26 papillary mesothelioma patients:
- 22 survived with no recurrence
- 1 patient experienced recurrence of WDPM after four years
- 3 patients died of other causes
Papillary mesothelioma has a low malignant potential. However, because research on WDPM is limited, long-term follow-ups and monitoring are recommended.
How Is Papillary Mesothelioma Treated?
Treatment is not always required for benign WDPM. However, treatment options for papillary mesothelioma may include:
- Surgical removal of the tumor
- Cytoreductive surgery (CRS)
- Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC)
- Early postoperative intraperitoneal chemotherapy (EPIC)
- Immunotherapy
- Multimodal treatment
Treatment for well-differentiated papillary mesothelioma depends on malignancy. Benign mesothelioma tumors are typically removed with complete surgical resection.
Ultimately, more research is needed for a standard treatment plan for papillary mesothelioma. Patients should seek professional medical advice to establish an individualized mesothelioma treatment plan.
Common Questions About Papillary Mesothelioma
-
How is a well-differentiated papillary mesothelial tumor treated?
Benign papillary mesothelioma may not require treatment. But doctors may use several different treatment methods when medical intervention is required. Surgery is the most common in case reports. But doctors may also recommend immunotherapy, chemotherapy or a combination of therapies.
-
What is the prognosis for papillary mesothelioma?
Papillary mesothelioma generally has a favorable prognosis. Patients may live for years or decades even without treatment. With treatment, papillary mesothelioma has a 5-year survival rate of 90%. Treatment may also help improve quality of life in cases where it is required.
-
What is well-differentiated papillary mesothelioma of the stomach?
Well-differentiated papillary mesothelioma (WDPM) affects the linings of different organs. It does not start in the stomach, but rather the lining of the abdomen. This is also known as the peritoneum. WDPM of the peritoneum is a rare type of cancer.
-
What is the survival rate for malignant papillary mesothelioma?
Data on survival rates for malignant papillary mesothelioma is difficult to come by because the disease is so rare. One case review found patients with WDPM of the pleura who received multimodal treatment had a 5-year survival rate of 90%. Another found those with WDPM of the peritoneum had a 10-year survival rate of over 30%.