What Is Mesothelioma Pathology?
Mesothelioma pathology is a branch of medical science that studies this rare cancer. It concentrates on understanding how malignant mesothelioma forms and progresses. Pathology is also a vital part of the mesothelioma diagnostic process. Many lab tests used to diagnose mesothelioma fall into the pathology category.
Why Does Pathology Matter for Mesothelioma Patients?
Pathology serves two important purposes for mesothelioma patients. First, it helps doctors arrive at an accurate diagnosis. Second, pathology can improve scientists’ understanding of how mesothelioma develops and advances. Both of these purposes can positively impact patients.
Doctors cannot confirm a mesothelioma diagnosis without pathology testing. A timely, correct diagnosis can help keep treatment options open for mesothelioma patients. Further, patients diagnosed at earlier stages of mesothelioma tend to have better life expectancy.
Pathology can also provide researchers with insights into the details of mesothelioma cells. These insights may go on to impact mesothelioma treatment and prognosis.
For example, researchers found a protein on the outside of several types of cancer cells in the 1990s. That protein is now called mesothelin, and mesothelioma cells make a lot of it. Scientists have used mesothelin to target new treatments directly at mesothelioma cells. A recent clinical trial took this approach for second-line treatment of pleural mesothelioma. Trial patients had a median survival of about two years. This means the new approach extended survival by more than one year compared to earlier approaches.
Resources for Mesothelioma Patients
What Do Mesothelioma Pathologists Study?
Mesothelioma pathologists study samples of tumor tissue to understand how the cancer grows. This can help them learn how asbestos causes mesothelioma. Mesothelioma pathology can also provide information about how the tumors spread throughout the body (metastasize).
Pathology studies have already helped researchers improve mesothelioma treatment. Additional mesothelioma research may continue on the same path.
Understanding What Causes Mesothelioma
Asbestos exposure causes malignant mesothelioma. Scientists have not yet determined every detail of this process. But they have identified the following steps:
- A person inhales or ingests asbestos fibers, which migrate to the mesothelium. The mesothelium is a type of tissue that lines several body cavities.
- The fibers irritate mesothelial cells, causing inflammation.
- Inflammation activates signaling pathways like the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kB) pathway.
- NF-kB or similar pathways increase the survival and growth of mesothelial cells.
- These changes activate oncogenes, which are genes that encourage or cause cancer. These changes may also damage or destroy tumor suppressor genes, which are genes that prevent cancer.
- Combined, these changes may cause normal mesothelial cells to become cancerous.
Experts generally agree that asbestos causes these events and leads to mesothelioma. But many aspects of mesothelioma development remain unknown. A deeper understanding of this process may one day lead to better treatments or possibly prevention of mesothelioma. Research into this topic is ongoing.
Understanding How Mesothelioma Progresses
Pathologists also study how mesothelioma grows and spreads. This aspect of cancer cell behavior differs from the processes that cause healthy cells to become cancerous. Progression involves growth of a single cancer cell into a tumor. It can also involve cells breaking away to form a new tumor in a different location.
Pleural mesothelioma is the most common form of this rare cancer. It forms in the pleura (the lining around the lungs). Researchers have described the progression of pleural mesothelioma as follows:
- A small tumor forms on the parietal pleura (the outermost layer). This tumor may look like a small nodule.
- More small tumors extend along the pleural surface.
- Tumors become so extensive that they cause the two layers of the pleura to stick together in places.
- Continued tumor growth encloses the lung on the affected side.
Peritoneal mesothelioma arises in the lining of the abdomen. It is more rare than pleural mesothelioma. This makes it difficult to diagnose early and study. This may be why researchers know less about peritoneal mesothelioma pathology than pleural.
Regardless of mesothelioma location, progression can have an impact on treatment and life expectancy. Doctors commonly determine the stage of mesothelioma before making a treatment plan. Less progression generally indicates an earlier stage. Earlier stages of mesothelioma tend to have better prognosis and treatment options.
Any patient hoping to understand how progression may affect them can discuss it with a mesothelioma doctor.
Mesothelioma Histopathology for Accurate Diagnosis
A definitive mesothelioma diagnosis requires histopathology testing. This involves examining tissue samples collected through a biopsy procedure. Histopathology explores how mesothelioma affects tissues in the areas where it develops.
Mesothelioma can be categorized by type, depending on its location.
The main types of mesothelioma develop in the:
- Pleura: Mesothelioma can arise in the lining around the lungs. This form is called pleural mesothelioma.
- Peritoneum: Mesothelioma can arise in the lining of the abdomen. This form is called peritoneal mesothelioma.
- Pericardium: Mesothelioma can arise in the lining around the heart. This form is called pericardial mesothelioma.
- Tunica vaginalis: Mesothelioma can arise in the lining around the testis. This form is called testicular mesothelioma.
Pathologists use one or more staining techniques to help identify mesothelioma cells and tumors. If doctors suspect a particular condition, that may influence their choice of staining techniques.
Immunohistochemistry for Mesothelioma Diagnosis
Immunohistochemistry is a histology technique. Doctors use it to help confirm a mesothelioma diagnosis. Immunohistochemistry uses antibodies and dyes to analyze cells and tissues. It may also be called immunostaining.
Antibodies are molecules that stick to a protein tied to a specific type of cell. Special dyes can interact with the antibodies to show the location of the target protein. These target proteins may be called immunohistochemical markers or antigens.
Some immunohistochemical markers are associated with mesothelioma and others are not. Testing for mesothelioma markers can help confirm a mesothelioma diagnosis. Testing for markers not associated with the cancer can help rule out a mesothelioma diagnosis.
Doctors may not always test for mesothelioma markers. Patients with a known history of asbestos exposure should disclose this to their doctors. Those who think they may have been exposed should do the same. This information can help their doctors choose appropriate tests.
Hematoxylin-Eosin Staining to Support a Diagnosis
Hematoxylin-eosin (H&E) staining may help pathologists diagnose mesothelioma. Hematoxylin is a blue dye that stains DNA in the center of a cell. Eosin is a pink dye that stains the outer layer of a cell, helping to show the cell’s size and shape.
Together, H&E dyes can help pathologists see the shape of cells. This can help support a mesothelioma diagnosis. It can also help determine a patient’s mesothelioma cell type.
H&E staining, along with other histology tests, can help doctors diagnose mesothelioma.
Mesothelioma Cytopathology in the Diagnostic Process
Cytology is the study of individual cells. Cytopathology is the study of individual cells affected by diseases, including mesothelioma.
Mesothelioma cytology is a form of cytopathology focused on mesothelioma cells. Patients may see the terms mesothelioma cytology and mesothelioma cytopathology used interchangeably.
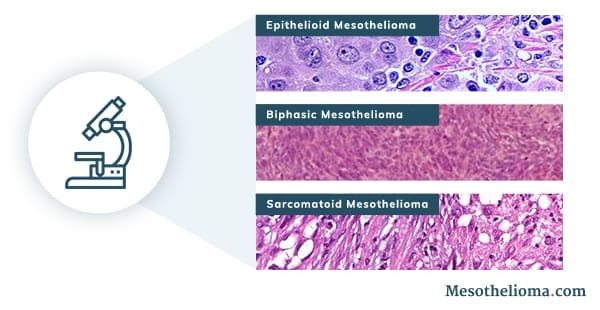
Cytology testing can help pathologists identify specific mesothelioma cell types. Mesothelioma occurs in three main cell types:
- Epithelioid mesothelioma: This is the most common mesothelioma cell type. Epithelioid cells form in sheet or cord structures. They may have an oval, cube-like or polygon-like shape. Epithelioid mesothelioma cells may appear similar to epithelial cells, which are healthy cells that line many tissues.
- Sarcomatoid mesothelioma: This is the least common mesothelioma cell type. Sarcomatoid cells appear spindle-like and form slender bundle shapes.
- Biphasic mesothelioma: This type is a combination of epithelioid and sarcomatoid cells.
Mesothelioma also occurs in rare cell types. These are subtypes of epithelioid, sarcomatoid and biphasic mesothelioma. Scientists may use cytology testing to determine a person’s mesothelioma cell type. This information can impact prognosis because the cell types do not respond to treatment equally.
Cytopathology’s Role in Diagnosis
Cytopathology can play a useful role in mesothelioma diagnosis. Mesothelioma tumors commonly cause symptoms due to fluid accumulation (effusion). In many cases, doctors recommend removing and testing this fluid. This type of procedure is known as a fluid biopsy. It is one of several mesothelioma biopsy procedures.
Doctors may order a fluid biopsy to examine potential tumor cells from effusion fluid. This type of testing may help determine the cause of the effusion. However, cytology testing of effusion fluid cannot diagnose mesothelioma on its own. Experts explain cytology testing alone cannot diagnose the cancer because:
- Sarcomatoid cells do not generally shed into effusion fluid.
- Obtaining an adequate sample of effusion fluid may be difficult.
- Certain benign conditions may have cells that appear very similar to mesothelioma.
Cytopathology analysis of effusion fluid may not be able to differentiate between mesothelioma and benign mesothelial hyperplasia. Benign mesothelial hyperplasia is a non-cancerous condition that affects mesothelial cells.
If doctors suspect either condition, they may use additional tests to rule one out or in. The additional tests can help identify mutations linked to mesothelioma, including:
- CDKN2A gene mutations
- BAP1 gene mutations
Cytopathology alone is not enough to confirm a mesothelioma diagnosis but may play a helpful role in the process.
Steps After an Accurate Mesothelioma Diagnosis
Doctors can use mesothelioma pathology to confirm or rule out mesothelioma. Once mesothelioma is confirmed, the care team can put together a fitting treatment plan for the individual. A timely, correct diagnosis may help keep a patient’s treatment options open. Aggressive treatment can extend survival and improve quality of life.