01. Biphasic Mesothelioma Explained
What Is Biphasic Mesothelioma?
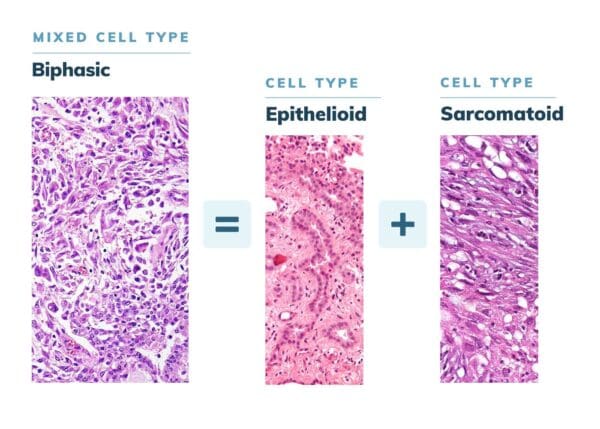
Biphasic mesothelioma is a specific cell type of mesothelioma cancer. Like all mesothelioma types, biphasic mesothelioma is caused by asbestos exposure. About 20% of all mesothelioma cancers are biphasic. Biphasic mesothelioma is a combination of epithelioid and sarcomatoid cells. Specifically, biphasic mesothelioma is any mesothelioma containing at least 10% of both epithelioid and sarcomatoid cells.
Biphasic mesothelioma primarily occurs in the pleura (lung linings) or peritoneum (abdominal lining). Biphasic mesothelioma tumors may sometimes form in the pericardium (heart lining) or tunica vaginalis (testes).
Regardless of the location, cell patterns depend on the amount of epithelioid and sarcomatoid cells. Epithelial and sarcomatoid cells have their own distinct characteristics.
The percentage of epithelioid and sarcomatoid cells in biphasic mesothelioma may impact treatment options and prognosis.
02. Symptoms of Biphasic Mesothelioma
Biphasic Mesothelioma Symptoms
Like all forms of malignant mesothelioma, symptoms may not present until decades after asbestos exposure.
Biphasic mesothelioma patients experience symptoms related to the location of their cancer. For example, patients with pleural biphasic mesothelioma may have lung-related symptoms.
Biphasic mesothelioma symptoms may include:
- Chest pain
- Pleural effusion
- Pleural plaques
- Pleural thickening
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
The biphasic cell type may also occur in peritoneal mesothelioma cases. Patients with peritoneal biphasic mesothelioma may experience abdominal pain, abdominal swelling and weight loss.
Patient factors, such as overall health, age and pre-existing conditions can also affect cancer symptoms.
03. Diagnosing Biphasic Mesothelioma
How Is Biphasic Mesothelioma Diagnosed?
A biphasic mesothelioma diagnosis may start with general exams and tests followed by imaging scans. This can include X-rays or CT scans. If these scans find visible tumors or excess fluid, the doctor may order a biopsy. Biopsy test results can confirm a biphasic mesothelioma diagnosis. They can also rule it out.
Doctors may also perform blood tests to identify specific biomarkers. These tests can help identify cancers and conditions with symptoms similar to mesothelioma. The number of tests performed varies by each patient.
Lastly, a mesothelioma biopsy is required for an accurate diagnosis. The biopsy sample has to contain at least 10% of both epithelial and sarcomatoid cells to be considered biphasic.
Biphasic mesothelioma has a combination of cell types. So, multiple biopsies may be needed for a pathologist to recognize the two types of cells.
Multiple Biopsies May Prevent Biphasic Mesothelioma Misdiagnosis
Biphasic tumors are not uniform, so the different cell types may be unevenly distributed. This means a single biopsy sample may not show the presence of both types of cells. In one study, more than 50% of tumors eventually diagnosed as biphasic were first mistakenly diagnosed as epithelioid. This was due to inadequate biopsy sample size.
One study noted the accuracy* of initial diagnosis depended on the type of biopsy:
*In this context, accuracy refers to the percentage of initial diagnoses from a given biopsy type that were the correct and final diagnosis for the patient.
Pathologists test biopsy tissue in various ways to confirm a biphasic mesothelioma diagnosis. This testing often includes immunohistochemistry to detect proteins made by sarcomatoid and epithelioid cells. If both types of proteins are found, the patient may have biphasic mesothelioma.
04. Treating Biphasic Mesothelioma
Biphasic Mesothelioma Treatment Options
Common biphasic mesothelioma treatments include chemotherapy and immunotherapy. Some patients also benefit from combination or multimodal treatments. A patient’s mesothelioma stage and tumor location can affect their treatment options. Those in good health may be eligible for surgery-based therapies.
Doctors have seen mixed results using chemotherapy and radiation for biphasic mesothelioma. Both therapies are largely ineffective for sarcomatoid cells. However, the therapies have shown some success in extending life expectancy for epithelioid mesothelioma.
Options for biphasic mesothelioma treatment may vary based on individual factors, like mesothelioma stage. Biphasic mesothelioma treatment may depend on factors including:
- Cancer location
- Overall patient health
- Percentage of sarcomatoid cells
- Severity of disease
Mesothelioma doctors will recommend the most appropriate treatment based on the individual patient.
Updates to Biphasic Mesothelioma Treatment Options
In the past, some researchers suggested all forms of biphasic mesothelioma should be treated with supportive or palliative care. But treatment advances and new mesothelioma drugs have led to more biphasic treatment options. Current research shows biphasic patients may live for years with treatment.
Biphasic Peritoneal Mesothelioma Treatment
One of the most successful treatments for peritoneal mesothelioma is cytoreductive surgery (CRS) combined with heated intraoperative chemotherapy (HIPEC).
In the past, doctors generally did not offer this treatment to patients with biphasic mesothelioma. Instead, these cases were treated as if they were sarcomatoid. Sarcomatoid does not respond well to some treatments and may metastasize, or spread.
In 2018, researchers found greater success when treating biphasic patients. Those treated with CRS + HIPEC did respond well to treatment.
Median Survival of Biphasic Peritoneal Mesothelioma Patients Treated With CRS & HIPEC |
|
|---|---|
| Surgery Success | Median Survival |
| Removal of All Tumors | 6.8 years |
| Removal of Most Tumors | 2.8 years |
Based on their findings, the researchers recommend aggressive treatment for patients likely to have successful CRS surgeries. Patients should discuss their eligibility for CRS with their oncologists.
Biphasic Pleural Mesothelioma Treatment
Biphasic malignant pleural mesothelioma patients have responded well to immunotherapy treatment. This cutting-edge treatment has delivered promising results for many patients. Doctors can explain if this is an option for their patients.
For example, researchers have studied pleural mesothelioma patients previously treated with chemotherapy. These patients experienced extended survival when later treated with immunotherapy. Some biphasic pleural mesothelioma patients survived 20 months or more while continuing treatment with Opdivo® (nivolumab).
In another study, patients with inoperable pleural mesothelioma were treated with two checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). The biphasic and sarcomatoid patients who received ICIs lived more than twice as long as those who had chemo instead.
Patients and their loved ones may also talk to their doctor about eligibility for potential clinical trials. These may offer benefits, like extended life expectancy.
05. Biphasic Mesothelioma Prognosis
Prognosis for Biphasic Mesothelioma
Biphasic mesothelioma survival ranges from about 1 – 3 years. However, survival varies depending on the location of the cancer and the chosen course of treatment:
Some recent studies involving cutting-edge treatments have reported longer survival times. For example, one study reported biphasic mesothelioma patients surviving nearly 7 years.
A biphasic mesothelioma prognosis varies patient-by-patient. This variance in prognosis depends on many factors. For example, the ratio of epithelioid and sarcomatoid cells can impact prognosis. Another contributing factor is the location of the tumors.
Depending on various factors, patients may have different treatment options and outcomes. Doctors can explain their patients’ prognoses and answer any questions they have.
Resources for Mesothelioma Patients
06. Common Questions
Common Questions About Biphasic Mesothelioma
-
What is the prognosis for biphasic mesothelioma?
- The prognosis varies for biphasic mesothelioma, with median survival ranging from about 1 – 3 years. Factors like the ratio of cell types may impact this. But some treatment methods are improving prognosis. For example, immunotherapy and CRS + HIPEC have achieved significant improvements in survival.
-
Is surgery an effective treatment for biphasic mesothelioma?
- Surgery, when combined with other treatments, has shown promise in treating biphasic mesothelioma. For example, a 2018 study treated mesothelioma with surgery (CRS) and chemotherapy (HIPEC). Some patients had biphasic mesothelioma. When doctors could remove all tumors, median survival was ~7 years.