01. Overview of Desmoplastic Mesothelioma
What Is Desmoplastic Mesothelioma?
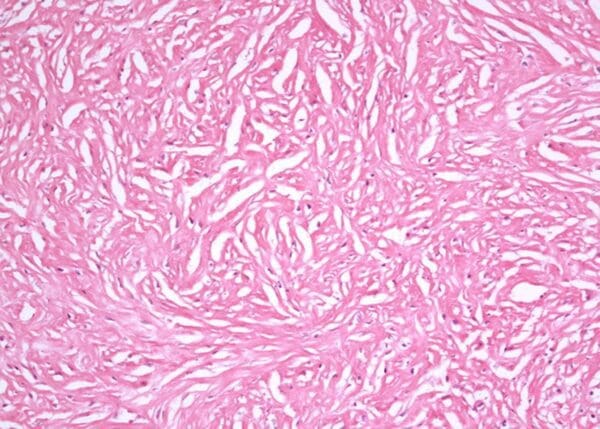
Desmoplastic mesothelioma is a less common form of malignant mesothelioma. Specifically, it is a subtype of sarcomatoid mesothelioma. Most forms of mesothelioma, including desmoplastic, are linked to asbestos exposure.
Desmoplastic mesothelioma cells may develop in different areas of the body. They are most often found with malignant pleural mesothelioma, which develops in the lung lining. Desmoplastic mesothelioma has also been found in cases of peritoneal and pericardial mesothelioma.
Mesothelioma occurs in three main cell types:
- Biphasic: This is a combination of epithelioid and sarcomatoid cells, also called mixed mesothelioma.
- Epithelial: This is a cell type that lines many tissues. Mesothelioma occurs most often in this cell type.
- Sarcomatoid: This is a less common mesothelioma cell type. Sarcomatoid cells, or spindle cells, have an elongated shape.
Each of the three cell types have their own subtypes. Desmoplastic malignant mesothelioma (DMM) is a rare subtype of sarcomatoid mesothelioma.
02. Prognosis for Desmoplastic Mesothelioma
Survival and Prognosis for Desmoplastic Mesothelioma
A desmoplastic mesothelioma prognosis may vary for each patient. Because of its rarity, there are few published studies around survival for desmoplastic mesothelioma. Some studies reported life expectancy ranging from about 1 – 12 months for patients who underwent treatment.
Desmoplastic mesothelioma is quite rare. So researchers have studied fewer cases than some other mesothelioma types. As such, it is unclear how desmoplastic survival rates compare to general mesothelioma survival rates.
Research on other mesothelioma types may provide some insight for desmoplastic mesothelioma survival time. Desmoplastic sarcomatoid mesothelioma is a non-epithelioid cell type. This means non-epithelioid research findings may apply to desmoplastic mesothelioma patients.
For example, a recent clinical trial treated non-epithelioid mesothelioma patients with immunotherapy. For these patients, the trial achieved a median survival of 18.1 months. Although possible, it is unclear if any participants had desmoplastic mesothelioma. Still, the results may be encouraging for those diagnosed with this subtype.
Doctors cannot yet estimate how immunotherapy may affect desmoplastic mesothelioma prognosis and survival. But future studies and case reports may provide this insight.
After a mesothelioma diagnosis, a doctor can provide individualized care for a patient. This includes estimating a mesothelioma prognosis and treatment plan based on various disease factors.
Resources for Mesothelioma Patients
03. Symptoms of Desmoplastic Mesothelioma
Desmoplastic Mesothelioma Symptoms
Desmoplastic mesothelioma is rare, and few studies have reported specific symptoms for it. In those publications, patients had symptoms similar to those of more common types.
Some symptoms associated with desmoplastic mesothelioma are also related to other conditions. For example, a respiratory infection could cause some of the same symptoms. Patients should discuss any potential mesothelioma symptoms with their doctors. This is especially important for any patients with a known history of asbestos exposure. Their doctor may be able to run tests to determine the cause of the symptoms.
04. Diagnosing Desmoplastic Mesothelioma
Desmoplastic Mesothelioma Diagnosis
Diagnosing desmoplastic mesothelioma is similar to diagnosing mesothelioma in general. Doctors may conduct various imaging scans and biopsies to make a diagnosis. However, this form of mesothelioma requires extra care with histology and cytology testing. These pathology tests involve microscopic analyses of specific cell types.
If doctors suspect malignant mesothelioma, the diagnostic process may include:
- CT scan: This is an imaging test to help identify various details of a patient’s cancer. CT scans can show abnormalities in normal organs and tissues.
- Fluid biopsy: This is a fluid sample removed with a needle for diagnostic analysis. Fluid samples may not be enough to confirm the presence of mesothelioma.
- Tissue biopsy: This is a tissue sample removed for diagnostic analysis. There are various methods a doctor can use to remove the sample.
A biopsy is the only way to confirm a mesothelioma diagnosis. Doctors may use a combination of tests to determine disease type, stage and other characteristics.
Part of the diagnostic process may involve determining the patient’s mesothelioma stage. The stage alone does not dictate life expectancy or prognosis. It does, however, help doctors choose the optimal treatment for the patient.
Misdiagnosis of Desmoplastic Mesothelioma
Desmoplastic mesothelioma can be difficult to distinguish from another condition called pleural fibrosis. The condition is also called fibrous pleurisy. Desmoplastic mesothelioma and pleural fibrosis both develop in the chest wall. These two conditions have other similarities as well.
Pleural fibrosis affects the thin lung lining, called the pleura. This condition causes the pleura to develop scar tissue. Pleural fibrosis may cause a variety of symptoms.
Both desmoplastic mesothelioma and pleural fibrosis cause the development of fibrous scar tissue. Because of this, doctors may confuse the two conditions for each other. Careful analysis of biopsy tissue can help pathologists correctly identify desmoplastic mesothelioma. In general, this means using cytology and immunohistochemical markers during testing.
Patients diagnosed with pleural fibrosis may have a history of asbestos exposure. If so, it is important they share this information with their doctor. This can help doctors understand the need for more biopsy sample tests. These tests will help to either rule out or confirm desmoplastic malignant mesothelioma.
05. Treating Desmoplastic Mesothelioma
Desmoplastic Mesothelioma Treatment
Desmoplastic mesothelioma treatment varies for each patient. Doctors usually follow general mesothelioma treatment practices, personalized for a patient’s needs.
Specific treatment approaches depend on several factors. These include tumor location, stage at diagnosis and overall patient health.
Regardless of the specific stage and location, palliative care is available throughout a patient’s mesothelioma journey. Palliative care methods can help patients manage symptoms, side effects and emotional needs.
There are many possible treatment options for mesothelioma patients. A mesothelioma doctor or expert can recommend the best options for each patient.
06. Causes of Desmoplastic Mesothelioma
How Does Asbestos Cause Desmoplastic Mesothelioma?
Asbestos is a known cause of malignant mesothelioma. However, some details specific to desmoplastic mesothelioma are unknown. The rarity of this subtype makes it difficult for scientists to study. Asbestos exposure may cause this subtype to develop like other forms of mesothelioma. Still, researchers have not determined exactly how it develops after asbestos exposure.
There are various published case reports on desmoplastic mesothelioma patients. Some of these case reports show numerous patients have an asbestos exposure history. These cases may have developed the same way researchers have suggested mesothelioma does in the pleura.
For instance, inhaling asbestos fibers may cause the fibers to move through lung tissue and lodge in the pleura. The fibers then cause inflammation, which may later lead to the development of mesothelioma tumor cells.
Patients should discuss any possible symptoms of mesothelioma with a doctor. It is also important for patients to disclose any history of asbestos exposure. With this information, doctors can begin to provide an accurate diagnosis.
Some symptom-free individuals may suspect or know of past asbestos exposure. They should still discuss this with a doctor, who may help monitor for signs of asbestos disease.
07. Common Questions
Common Questions About Desmoplastic Mesothelioma
-
What is sarcomatoid desmoplastic mesothelioma?
- Desmoplastic mesothelioma is a rare subtype of malignant sarcomatoid mesothelioma. It may be caused by asbestos exposure. Symptoms include breathing difficulties and chest pain. Patients may benefit from chemotherapy or immunotherapy treatment.
-
How do doctors treat desmoplastic mesothelioma?
- Doctors may treat desmoplastic mesothelioma with chemotherapy, immunotherapy or combination treatments. In medical studies, chemotherapy is the most commonly reported treatment.